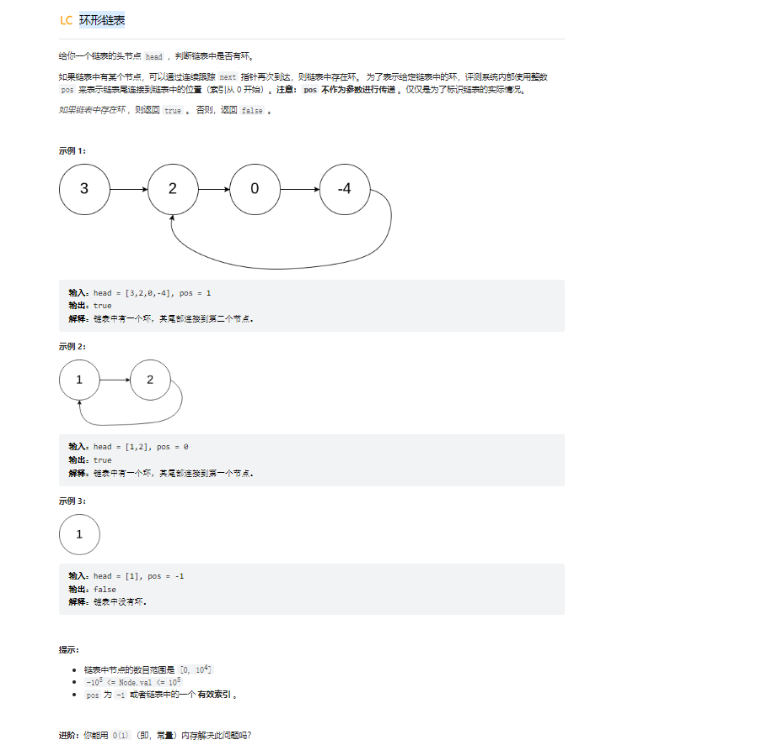
原题出处:https://leetcode.cn/leetbook/read/top-interview-questions-easy/xnwzei/
解法一:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}思路:快慢指针,如果存在环,那么快慢指针就一定会相遇,就好像秒针和分针,总会相遇。
解法二:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet();
while (head != null) {
if (set.contains(head)) {
return true;
}
set.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}思路:每走一步都先判断set集合中是否包含链表节点,如果包含则表示存在环,如没有包含,则将链表节点放到一个set集合中并将节点指向下一个。都没有包含,则表示当前链表中不存在环
解法三:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
if (head == head.next) {
return true;
}
ListNode node = head.next;
head.next = head;
return hasCycle(node);
}
}思路:递归链表,每一次都将链表的下一个引用指向自己,如果存在环,那么递归的是否一定会再次找到下一个引用指向自己的节点。