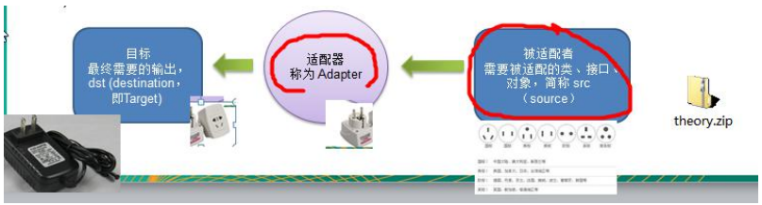
1、现实生活中的适配器例子
泰国插座用的是两孔的(欧标),可以买个多功能转换插头(适配器),这样就可以使用了。

2、基本介绍
1)适配器模式(Adapter Pattern)将某个类的接口转换成客户端期望的另一个接口表示,主的目的是兼容性,让原本
因接口不匹配不能一起工作的两个类可以协同工作。其别名为包装器(Wrapper)
2)适配器模式属于结构型模式
3)主要分为三类:类适配器模式、对象适配器模式、接口适配器模式
3、工作原理
1)适配器模式:将一个类的接口转换成另一种接口.让原本接口不兼容的类可以兼容
2)从用户的角度看不到被适配者,是解耦的
3)用户调用适配器转化出来的目标接口方法,适配器再调用被适配者的相关接口方法
4)用户收到反馈结果,感觉只是和目标接口交互,如图
4、类适配器模式
4.1类适配器模式介绍
基本介绍: Adapter类,通过继承src类,实现 dst 类接口,完成src->dst的适配。
4.2类适配器模式应用实例
1)应用实例说明
以生活中充电器的例子来讲解适配器,充电器本身相当于Adapter,220V交流电相当于src(即被适配者),我们的目dst(即目标)是5V直流电
2)思路分析(类图)
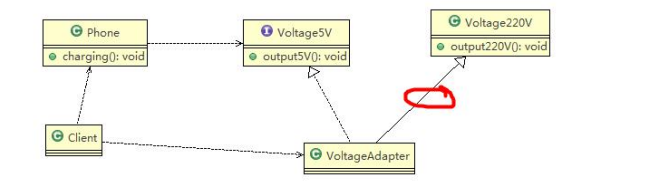
3)代码实现
项目截图:
Client:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(" === 类适配器模式 ====");
Phone phone = new Phone();
phone.charging(new VoltageAdapter());
}
}IVoltage5V:
//适配接口
public interface IVoltage5V {
public int output5V();
}
Phone:
public class Phone {
//充电
public void charging(IVoltage5V iVoltage5V) {
if(iVoltage5V.output5V() == 5) {
System.out.println("电压为5V, 可以充电~~");
} else if (iVoltage5V.output5V() > 5) {
System.out.println("电压大于5V, 不能充电~~");
}
}
}
Voltage220V:
//被适配的类
public class Voltage220V {
//输出220V的电压
public int output220V() {
int src = 220;
System.out.println("电压=" + src + "伏");
return src;
}
}VoltageAdapter:
//适配器类
public class VoltageAdapter extends Voltage220V implements IVoltage5V {
@Override
public int output5V() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//获取到220V电压
int srcV = output220V();
int dstV = srcV / 44 ; //转成 5v
return dstV;
}
}4.3、类适配器模式注意事项和细节
l) Java是单继承机制,所以类适配器需要继承src 类这一点算是一个缺点,因为这要求dst必须是接口,有一定局
限性;
2) src类的方法在Adaptcr 中都会暴露出来,也增加了使用的成本。
3)由于其继承了src类,所以它可以根据需求重写src类的方法,使得Adapter 的灵活性增强了。
5、对象适配器模式
5.1对象适配器模式介绍
l)基本思路和类的适配器模式相同,只是将Adapter类作修改,不是继承src类,而是持有src类的实例,以解决
兼容性的问题。即:持有src类,实现 dst类接口,完成src->dst的适配
2)根据“合成复用原则”,在系统中尽量使用关联关系(聚合)来代继承关系。
3)对象适配器模式是适配器模式常用的一种
5.2对象适配器模式应用实例
1)应用实例说明
以生活中充电器的例子来讲解适配器,充电器本身相当于Adapter,220V交流电相当于src(即被适配者),我们的目dst(即目标)是5V直流电,使用对象适配器模式完成。
2)思路分析(类图):只需修改适配器即可,如下:
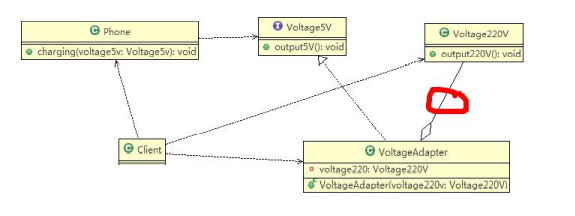
3)代码实现
Client:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(" === 对象适配器模式 ====");
Phone phone = new Phone();
phone.charging(new VoltageAdapter(new Voltage220V()));
}
}IVoltage5V:
//适配接口
public interface IVoltage5V {
public int output5V();
}
Phone:
public class Phone {
//充电
public void charging(IVoltage5V iVoltage5V) {
if(iVoltage5V.output5V() == 5) {
System.out.println("电压为5V, 可以充电~~");
} else if (iVoltage5V.output5V() > 5) {
System.out.println("电压大于5V, 不能充电~~");
}
}
}Voltage220V:
//被适配的类
public class Voltage220V {
//输出220V的电压,不变
public int output220V() {
int src = 220;
System.out.println("电压=" + src + "伏");
return src;
}
}VoltageAdapter:
//适配器类
public class VoltageAdapter implements IVoltage5V {
private Voltage220V voltage220V; // 关联关系-聚合
//通过构造器,传入一个 Voltage220V 实例
public VoltageAdapter(Voltage220V voltage220v) {
this.voltage220V = voltage220v;
}
@Override
public int output5V() {
int dst = 0;
if(null != voltage220V) {
int src = voltage220V.output220V();//获取220V 电压
System.out.println("使用对象适配器,进行适配~~");
dst = src / 44;
System.out.println("适配完成,输出的电压为=" + dst);
}
return dst;
}
}5.3、对象适配器模式注意事项和细节
1)对象适配器和类适配器其实算是同一种思想,只不过实现方式不同。
根据合成复用原则,使用组合替代继承,所以它解决了类适配器必须继承src的局限性问题,也不再要求dst必须是接口。
2)使用成本更低,更灵活。
6、接口适配器模式
6.1、接口适配器模式介绍
1)一些书籍称为:适配器模式(Default Adapter Pattern)或缺省适配器模式.
2)核心思路:当不需要全部实现接口提供的方法时,可先设计一个抽象类实现接口,并为该接口中每个方法提供
一个默认实现(空方法),那么该抽象类的子类可有选择地覆盖父类的某些方法来实现需求
3)适用于一个接口不想使用其所有的方法的情况。
6.2接口适配器模式应用实例
l) Android中的属性动画ValueAnimator类可以通过addListener(AnimatorListener listener)方法添加监听器,那么
常规写法如下:
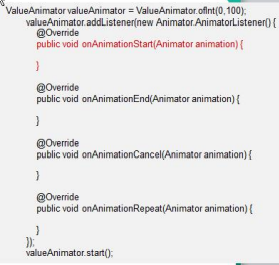
2)有时候我们不想实现Animator.AnimatorListener接口的全部方法,我们只想监听onAnimationStart,我们会如
下:

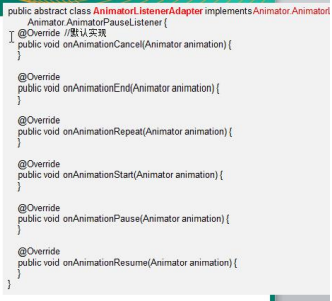
3) AnimatorListenerAdapter类,就是一个
接口适配器,代码如下:它空实现了Animator.AnimatorListener类(src)的所有方法.
4)AnimatorListener是一个接口.

5)程序里的匿名内部类就是Listener具体实现类

6)案例说明
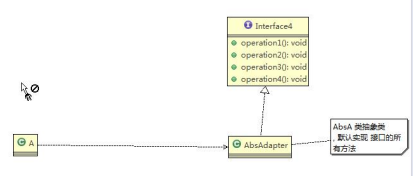
项目截图:
AbsAdapter:
//在AbsAdapter 我们将 Interface4 的方法进行默认实现
public abstract class AbsAdapter implements Interface4 {
//默认实现
public void m1() {
}
public void m2() {
}
public void m3() {
}
public void m4() {
}
}Client:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbsAdapter absAdapter = new AbsAdapter() {
//只需要去覆盖我们 需要使用 接口方法
@Override
public void m1() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("使用了m1的方法");
}
};
absAdapter.m1();
}
}
Interface4:
public interface Interface4 {
public void m1();
public void m2();
public void m3();
public void m4();
}
7、适配器模式在SpringMVC框架应用的源码剖析
1)SpringMvc中的HandlerAdapter,就使用了适配器模式
2) SpringMVC处理请求的流程回顾
3)使用HandlerAdapter的原因分析:
可以看到处理器的类型不同,有多重实现方式,那么调用方式就不是确定的,如果需要直接调用Controller方法,需要调用的时候就得不断是使用if else来进行判断是哪一种子类然后执行。那么如果后面要扩展Controller,就得修改原来的代码,这样违背了OCP原则.
4)代码分析+Debug源码
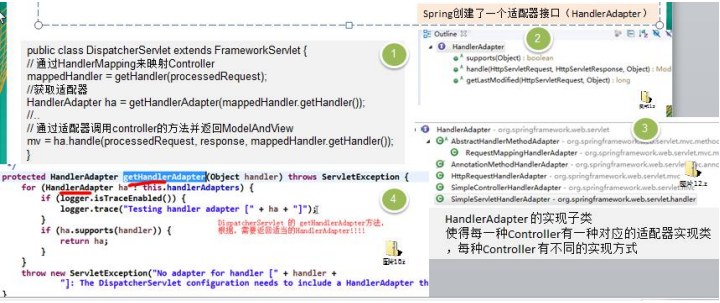
5)动手写SpringMVC通过适配器设计模式获取到对应的Controller的源码
说明:
Spring定义了一个适配接口,使得每一种Controller有一种对应的适配器实现类
适配器代替controller执行相应的方法
扩展Controller时,只需要增加一个适配器类就完成了SpringMVC的扩展了,这就是设计模式的力量

8、适配器模式的注意事项和细节
1)三种命名方式,是根据 src是以怎样的形式给到Adapter(在 Adapter里的形式)来命名的。
2)类适配器:以类给到,在 Adapter 里,就是将src当做类,继承
对象适配器:以对象给到,在Adapter 里,将src作为一个对象,持有接口适配器:以接口给到,在Adapter 里,将src作为一个接口,实现
3)Adapter模式最大的作用还是将原本不兼容的接口融合在一起工作。
4)实际开发中,实现起来不拘泥于我们讲解的三种经典形式
9、springmvc代码实现
项目截图:
Controller:
//多种Controller实现
public interface Controller {
}
class HttpController implements Controller {
public void doHttpHandler() {
System.out.println("http...");
}
}
class SimpleController implements Controller {
public void doSimplerHandler() {
System.out.println("simple...");
}
}
class AnnotationController implements Controller {
public void doAnnotationHandler() {
System.out.println("annotation...");
}
}DispatchServlet:
public class DispatchServlet {
public static List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<HandlerAdapter>();
public DispatchServlet() {
handlerAdapters.add(new AnnotationHandlerAdapter());
handlerAdapters.add(new HttpHandlerAdapter());
handlerAdapters.add(new SimpleHandlerAdapter());
}
public void doDispatch() {
// 此处模拟SpringMVC从request取handler的对象,
// 适配器可以获取到希望的Controller
HttpController controller = new HttpController();
// AnnotationController controller = new AnnotationController();
//SimpleController controller = new SimpleController();
// 得到对应适配器
HandlerAdapter adapter = getHandler(controller);
// 通过适配器执行对应的controller对应方法
adapter.handle(controller);
}
public HandlerAdapter getHandler(Controller controller) {
//遍历:根据得到的controller(handler), 返回对应适配器
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(controller)) {
return adapter;
}
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new DispatchServlet().doDispatch(); // http...
}
}HandlerAdapter:
///定义一个Adapter接口
public interface HandlerAdapter {
public boolean supports(Object handler);
public void handle(Object handler);
}
// 多种适配器类
class SimpleHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {
public void handle(Object handler) {
((SimpleController) handler).doSimplerHandler();
}
public boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof SimpleController);
}
}
class HttpHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {
public void handle(Object handler) {
((HttpController) handler).doHttpHandler();
}
public boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof HttpController);
}
}
class AnnotationHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {
public void handle(Object handler) {
((AnnotationController) handler).doAnnotationHandler();
}
public boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof AnnotationController);
}
}10、本人推荐的两本书:(这是本人在大学时期一直读的书,就算是现在也时常拿出来翻阅,很多东西,当时没明白,现在看的更加的清晰了)
uml
设计模式