1、搭建flutter的开发环境:http://www.haijin.xyz/article/730
2、创建一个项目:
flutter create layout
这个demo只是管页面布局,比较简单,所以我们只在main.dart中操作
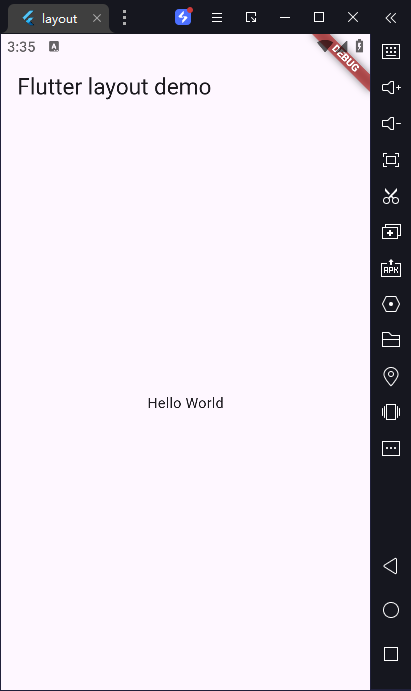
1)在屏幕中间输出“Hello World”
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(const MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
const String appTitle = 'Flutter layout demo';
return MaterialApp(
title: appTitle,
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text(appTitle),
),
body: const Center(
child: Text('Hello World'),
),
),
);
}
}
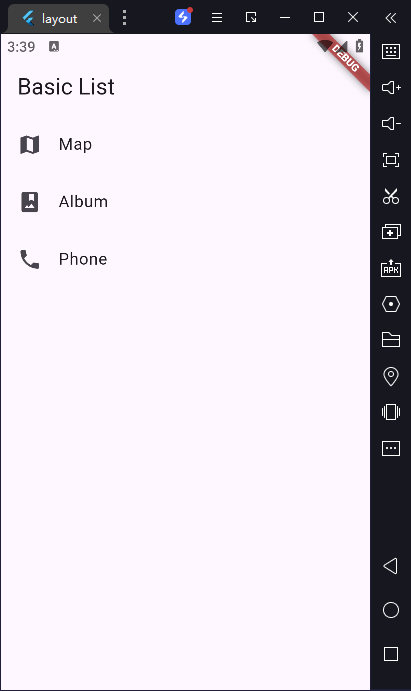
2)创建一个 ListView
使用标准的 ListView 构造方法非常适合只有少量数据的列表。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(const MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
const title = 'Basic List';
return MaterialApp(
title: title,
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text(title),
),
body: ListView(
children: const <Widget>[
ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.map),
title: Text('Map'),
),
ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.photo_album),
title: Text('Album'),
),
ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.phone),
title: Text('Phone'),
),
],
),
),
);
}
}
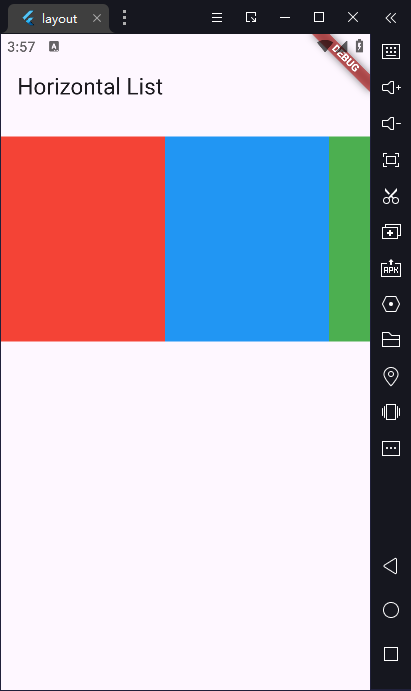
3)创建一个水平滑动的列表
有时,你可能想要创建一个水平滑动(而不是竖直滑动)的列表。 ListView widget 本身就支持水平列表的创建。
我们将会使用标准的 ListView 构造方法,通过指定 scrollDirection 的值为水平方向,来覆盖默认的竖直方向。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(const MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
const title = 'Horizontal List';
return MaterialApp(
title: title,
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text(title),
),
body: Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 20),
height: 200,
child: ListView(
// This next line does the trick.
scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal,
children: <Widget>[
Container(
width: 160,
color: Colors.red,
),
Container(
width: 160,
color: Colors.blue,
),
Container(
width: 160,
color: Colors.green,
),
Container(
width: 160,
color: Colors.yellow,
),
Container(
width: 160,
color: Colors.orange,
),
],
),
),
),
);
}
}
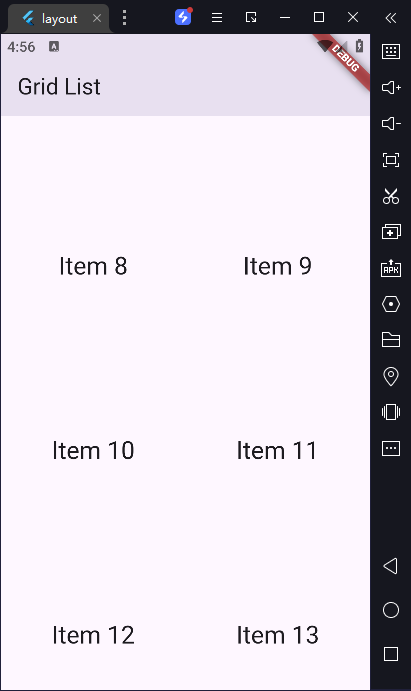
4) 创建一个网格列表
有时候,你可能希望用网格来展示内容,而不是一条接着一条的普通列表来展示。在本文当中,我们将采用 GridView widget。
用网格展示数据最简单的方式,就是通过使用 GridView.count() 构造方法,因为它允许我们指定有多少行多少列。
为了帮助我们想象 GridView 是如何工作的,在这个例子中,我们将创建一个包含有 100 个 widget 的 List,每个 Widget 将展示它在 List 中的索引。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
const title = 'Grid List';
return MaterialApp(
title: title,
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text(title),
),
body: GridView.count(
// Create a grid with 2 columns. If you change the scrollDirection to
// horizontal, this produces 2 rows.
crossAxisCount: 2,
// Generate 100 widgets that display their index in the List.
children: List.generate(100, (index) {
return Center(
child: Text(
'Item $index',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineSmall,
),
);
}),
),
),
);
}
}
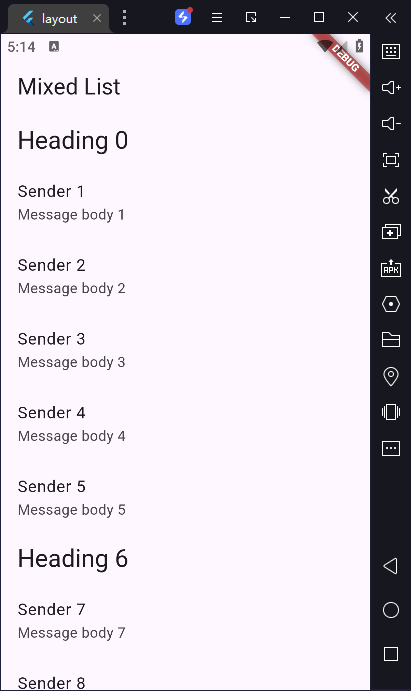
5)创建拥有不同列表项的列表
我们经常需要创建展示不同类型内容的列表。比方说,我们可能在开发一个列表,它显示一个标题,后跟一些与标题相关的项目,然后是另一个标题,依此类推。
你可以通过以下步骤,用 Flutter 创建这样的结构:
-
创建一个拥有不同类型项目的数据源
-
将数据源的数据转换成列表 widget
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(
MyApp(
items: List<ListItem>.generate(
1000,
(i) => i % 6 == 0
? HeadingItem('Heading $i')
: MessageItem('Sender $i', 'Message body $i'),
),
),
);
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
final List<ListItem> items;
const MyApp({super.key, required this.items});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
const title = 'Mixed List';
return MaterialApp(
title: title,
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text(title),
),
body: ListView.builder(
// Let the ListView know how many items it needs to build.
itemCount: items.length,
// Provide a builder function. This is where the magic happens.
// Convert each item into a widget based on the type of item it is.
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final item = items[index];
return ListTile(
title: item.buildTitle(context),
subtitle: item.buildSubtitle(context),
);
},
),
),
);
}
}
/// The base class for the different types of items the list can contain.
abstract class ListItem {
/// The title line to show in a list item.
Widget buildTitle(BuildContext context);
/// The subtitle line, if any, to show in a list item.
Widget buildSubtitle(BuildContext context);
}
/// A ListItem that contains data to display a heading.
class HeadingItem implements ListItem {
final String heading;
HeadingItem(this.heading);
@override
Widget buildTitle(BuildContext context) {
return Text(
heading,
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineSmall,
);
}
@override
Widget buildSubtitle(BuildContext context) => const SizedBox.shrink();
}
/// A ListItem that contains data to display a message.
class MessageItem implements ListItem {
final String sender;
final String body;
MessageItem(this.sender, this.body);
@override
Widget buildTitle(BuildContext context) => Text(sender);
@override
Widget buildSubtitle(BuildContext context) => Text(body);
}
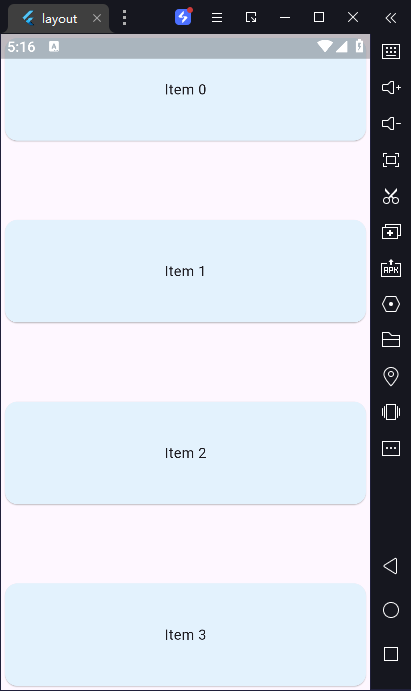
6) 用空格隔开的项目列表
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(const SpacedItemsList());
class SpacedItemsList extends StatelessWidget {
const SpacedItemsList({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
const items = 4;
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
theme: ThemeData(
colorScheme: ColorScheme.fromSeed(seedColor: Colors.deepPurple),
cardTheme: CardTheme(color: Colors.blue.shade50),
useMaterial3: true,
),
home: Scaffold(
body: LayoutBuilder(builder: (context, constraints) {
return SingleChildScrollView(
child: ConstrainedBox(
constraints: BoxConstraints(minHeight: constraints.maxHeight),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.stretch,
children: List.generate(
items, (index) => ItemWidget(text: 'Item $index')),
),
),
);
}),
),
);
}
}
class ItemWidget extends StatelessWidget {
const ItemWidget({
super.key,
required this.text,
});
final String text;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Card(
child: SizedBox(
height: 100,
child: Center(child: Text(text)),
),
);
}
}
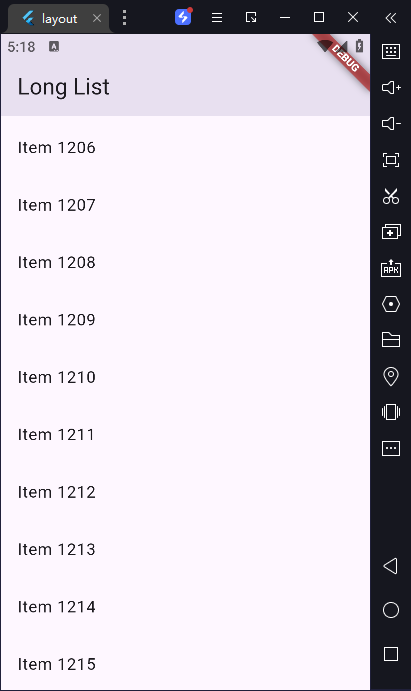
7)长列表的处理
标准的 ListView 构造函数适用于短列表,对于具有大量列表项的长列表,需要用 ListView.builder 构造函数来创建。
与标准的 ListView 构造函数需要一次性创建所有列表项不同的是, ListView.builder 构造函数只在列表项从屏幕外滑入屏幕时才去创建列表项。
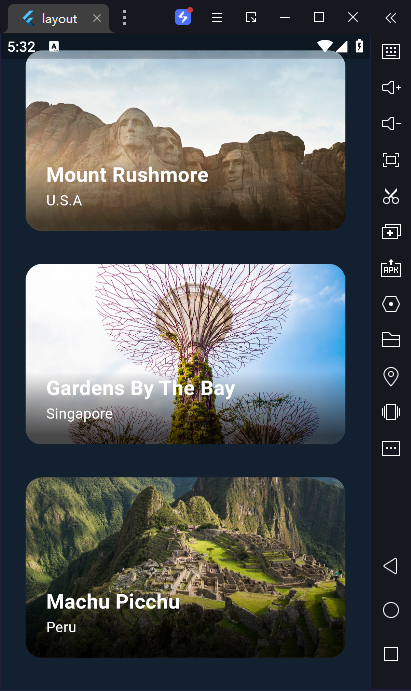
8)创建一个滚动视差效果
当你在应用程序中滚动卡片列表(例如包含图像)时,你可能会注意到这些图像看起来比屏幕上的其他部分滚动得慢。看起来好像列表中的卡片在前景中,但图像本身位于遥远的背景中。这种效果被称为视差。
在这个配方中,您通过构建一个卡片列表(圆角包含一些文本)来创建视差效果。每张卡片还包含一个图像。当卡片在屏幕上滑动时,每张卡片内的图像也会向下滑动。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/rendering.dart';
const Color darkBlue = Color.fromARGB(255, 18, 32, 47);
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
theme: ThemeData.dark().copyWith(scaffoldBackgroundColor: darkBlue),
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
home: const Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: ExampleParallax(),
),
),
);
}
}
class ExampleParallax extends StatelessWidget {
const ExampleParallax({
super.key,
});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return SingleChildScrollView(
child: Column(
children: [
for (final location in locations)
LocationListItem(
imageUrl: location.imageUrl,
name: location.name,
country: location.place,
),
],
),
);
}
}
class LocationListItem extends StatelessWidget {
LocationListItem({
super.key,
required this.imageUrl,
required this.name,
required this.country,
});
final String imageUrl;
final String name;
final String country;
final GlobalKey _backgroundImageKey = GlobalKey();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 24, vertical: 16),
child: AspectRatio(
aspectRatio: 16 / 9,
child: ClipRRect(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(16),
child: Stack(
children: [
_buildParallaxBackground(context),
_buildGradient(),
_buildTitleAndSubtitle(),
],
),
),
),
);
}
Widget _buildParallaxBackground(BuildContext context) {
return Flow(
delegate: ParallaxFlowDelegate(
scrollable: Scrollable.of(context),
listItemContext: context,
backgroundImageKey: _backgroundImageKey,
),
children: [
Image.network(
imageUrl,
key: _backgroundImageKey,
fit: BoxFit.cover,
),
],
);
}
Widget _buildGradient() {
return Positioned.fill(
child: DecoratedBox(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
gradient: LinearGradient(
colors: [Colors.transparent, Colors.black.withOpacity(0.7)],
begin: Alignment.topCenter,
end: Alignment.bottomCenter,
stops: const [0.6, 0.95],
),
),
),
);
}
Widget _buildTitleAndSubtitle() {
return Positioned(
left: 20,
bottom: 20,
child: Column(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
Text(
name,
style: const TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
Text(
country,
style: const TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 14,
),
),
],
),
);
}
}
class ParallaxFlowDelegate extends FlowDelegate {
ParallaxFlowDelegate({
required this.scrollable,
required this.listItemContext,
required this.backgroundImageKey,
}) : super(repaint: scrollable.position);
final ScrollableState scrollable;
final BuildContext listItemContext;
final GlobalKey backgroundImageKey;
@override
BoxConstraints getConstraintsForChild(int i, BoxConstraints constraints) {
return BoxConstraints.tightFor(
width: constraints.maxWidth,
);
}
@override
void paintChildren(FlowPaintingContext context) {
// Calculate the position of this list item within the viewport.
final scrollableBox = scrollable.context.findRenderObject() as RenderBox;
final listItemBox = listItemContext.findRenderObject() as RenderBox;
final listItemOffset = listItemBox.localToGlobal(
listItemBox.size.centerLeft(Offset.zero),
ancestor: scrollableBox);
// Determine the percent position of this list item within the
// scrollable area.
final viewportDimension = scrollable.position.viewportDimension;
final scrollFraction =
(listItemOffset.dy / viewportDimension).clamp(0.0, 1.0);
// Calculate the vertical alignment of the background
// based on the scroll percent.
final verticalAlignment = Alignment(0.0, scrollFraction * 2 - 1);
// Convert the background alignment into a pixel offset for
// painting purposes.
final backgroundSize =
(backgroundImageKey.currentContext!.findRenderObject() as RenderBox)
.size;
final listItemSize = context.size;
final childRect =
verticalAlignment.inscribe(backgroundSize, Offset.zero & listItemSize);
// Paint the background.
context.paintChild(
0,
transform:
Transform.translate(offset: Offset(0.0, childRect.top)).transform,
);
}
@override
bool shouldRepaint(ParallaxFlowDelegate oldDelegate) {
return scrollable != oldDelegate.scrollable ||
listItemContext != oldDelegate.listItemContext ||
backgroundImageKey != oldDelegate.backgroundImageKey;
}
}
class Parallax extends SingleChildRenderObjectWidget {
const Parallax({
super.key,
required Widget background,
}) : super(child: background);
@override
RenderObject createRenderObject(BuildContext context) {
return RenderParallax(scrollable: Scrollable.of(context));
}
@override
void updateRenderObject(
BuildContext context, covariant RenderParallax renderObject) {
renderObject.scrollable = Scrollable.of(context);
}
}
class ParallaxParentData extends ContainerBoxParentData<RenderBox> {}
class RenderParallax extends RenderBox
with RenderObjectWithChildMixin<RenderBox>, RenderProxyBoxMixin {
RenderParallax({
required ScrollableState scrollable,
}) : _scrollable = scrollable;
ScrollableState _scrollable;
ScrollableState get scrollable => _scrollable;
set scrollable(ScrollableState value) {
if (value != _scrollable) {
if (attached) {
_scrollable.position.removeListener(markNeedsLayout);
}
_scrollable = value;
if (attached) {
_scrollable.position.addListener(markNeedsLayout);
}
}
}
@override
void attach(covariant PipelineOwner owner) {
super.attach(owner);
_scrollable.position.addListener(markNeedsLayout);
}
@override
void detach() {
_scrollable.position.removeListener(markNeedsLayout);
super.detach();
}
@override
void setupParentData(covariant RenderObject child) {
if (child.parentData is! ParallaxParentData) {
child.parentData = ParallaxParentData();
}
}
@override
void performLayout() {
size = constraints.biggest;
// Force the background to take up all available width
// and then scale its height based on the image's aspect ratio.
final background = child!;
final backgroundImageConstraints =
BoxConstraints.tightFor(width: size.width);
background.layout(backgroundImageConstraints, parentUsesSize: true);
// Set the background's local offset, which is zero.
(background.parentData as ParallaxParentData).offset = Offset.zero;
}
@override
void paint(PaintingContext context, Offset offset) {
// Get the size of the scrollable area.
final viewportDimension = scrollable.position.viewportDimension;
// Calculate the global position of this list item.
final scrollableBox = scrollable.context.findRenderObject() as RenderBox;
final backgroundOffset =
localToGlobal(size.centerLeft(Offset.zero), ancestor: scrollableBox);
// Determine the percent position of this list item within the
// scrollable area.
final scrollFraction =
(backgroundOffset.dy / viewportDimension).clamp(0.0, 1.0);
// Calculate the vertical alignment of the background
// based on the scroll percent.
final verticalAlignment = Alignment(0.0, scrollFraction * 2 - 1);
// Convert the background alignment into a pixel offset for
// painting purposes.
final background = child!;
final backgroundSize = background.size;
final listItemSize = size;
final childRect =
verticalAlignment.inscribe(backgroundSize, Offset.zero & listItemSize);
// Paint the background.
context.paintChild(
background,
(background.parentData as ParallaxParentData).offset +
offset +
Offset(0.0, childRect.top));
}
}
class Location {
const Location({
required this.name,
required this.place,
required this.imageUrl,
});
final String name;
final String place;
final String imageUrl;
}
const urlPrefix =
'https://docs.flutter.dev/cookbook/img-files/effects/parallax';
const locations = [
Location(
name: 'Mount Rushmore',
place: 'U.S.A',
imageUrl: '$urlPrefix/01-mount-rushmore.jpg',
),
Location(
name: 'Gardens By The Bay',
place: 'Singapore',
imageUrl: '$urlPrefix/02-singapore.jpg',
),
Location(
name: 'Machu Picchu',
place: 'Peru',
imageUrl: '$urlPrefix/03-machu-picchu.jpg',
),
Location(
name: 'Vitznau',
place: 'Switzerland',
imageUrl: '$urlPrefix/04-vitznau.jpg',
),
Location(
name: 'Bali',
place: 'Indonesia',
imageUrl: '$urlPrefix/05-bali.jpg',
),
Location(
name: 'Mexico City',
place: 'Mexico',
imageUrl: '$urlPrefix/06-mexico-city.jpg',
),
Location(
name: 'Cairo',
place: 'Egypt',
imageUrl: '$urlPrefix/07-cairo.jpg',
),
];